Portal:Chemistry
|
edit
The Chemistry Portal
Welcome to the chemistry portal. Chemistry is a branch of science. Modern chemistry focuses on the study of elements of the world and the bonds between elements. Chemistry also deals with composition, structure, and properties of substances and the transformations that they undergo. In the study of matter, chemistry also investigates its interactions with energy and itself. Because of the diversity of matter, which is mostly in the form of compounds, chemists often study how atoms of different chemical elements interact to form molecules, and how molecules interact with each other.
edit
Featured article
Caffeine is a xanthine alkaloid compound that acts as a stimulant in humans. Caffeine is sometimes called guaranine when found in guarana, mateine when found in mate, and theine when found in tea. It is found in the leaves and beans of the coffee plant, in tea, yerba mate, and guarana berries, and in small quantities in cocoa, the kola nut and the Yaupon Holly. Overall, caffeine is found in the beans, leaves, and fruit of over 60 plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding upon them.
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant, having the effect of temporarily warding off drowsiness and restoring alertness. Beverages containing caffeine, such as coffee, tea, soft drinks and energy drinks enjoy great popularity: caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive substance. In North America, 90% of adults consume caffeine daily. Many natural sources of caffeine also contain widely varying mixtures of other xanthine alkaloids, including the cardiac stimulants theophylline and theobromine and other substances such as tannins.
edit
Selected biography
Amedeo Avogadro (1776-1856) was an Italian chemist, most noted for his contributions to the theory of molarity and molecular mass. Avogadro's law implies that the relationship occurring between the weights of same volumes of different gases (at the same temperature and pressure) corresponds to the relationship between respective molecular weights. Hence, relative molecular masses can be calculated from the masses of gas samples. One of the most important contributions of Avogadro's work was clearly distinguishing atoms from molecules, admitting that simple particles too could be composed of molecules, and that these are composed of atoms.
edit
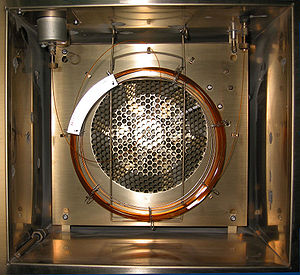
Selected pictureGas chromatography is an important type of chromatography used in chemical analysis. A volatile substance or mixture is injected and carried down a column (the coil shown) to a detector, which records the amount and the time on the column for each component. An oven (shown here with the door open) maintains the column at a desired temperature. edit
Periodic Table
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||