Local government in Wales
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children, which runs nearly 200 sos schools in the developing world, organised this selection. SOS Children has looked after children in Africa for forty years. Can you help their work in Africa?
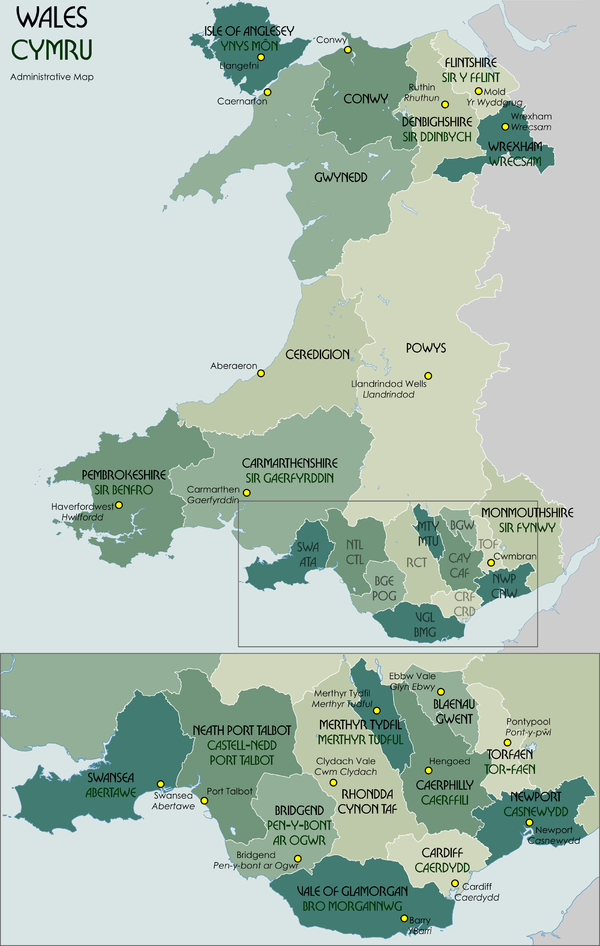
For local government purposes, Wales is divided into 22 unitary authority areas, which are responsible for the provision of all local government services, including education, social work, environment and roads services. Below these in some areas there are community councils, which cover specific areas within a council area. The unitary authority areas are referred to in local government legislation as the principal areas of Wales. They are variously styled: nine areas are styled as counties, three as cities (two of which as City and County), and ten as county boroughs, although all authorities have equal powers. All 22 authorities are regularly called counties in the Welsh media, including BBC Wales. They came into being on 1 April 1996 by virtue of the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994 (1994 c. 19).
The Queen appoints a Lord Lieutenant to represent her in the eight Preserved counties of Wales — which are combinations of council areas. However other subdivisions occur when dividing Wales into separate regions in the provisions of fire, and police services. For example there is a South Wales Police force, rather than the Glamorgan Police Force.
Cities
There are five cities in total in Wales: in addition to the three unitary authorities with city status, the communities of Bangor and St David's also have the status. City status is determined by letters patent.
- Bangor
- Cardiff
- Newport
- St David's
- Swansea
St. Asaph, as the seat of a bishopric, was historically referred to as a city, and was described as such in the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica. The status was never officially recognised, however. When city status was restored to St David's in 1994, St Asaph community council submitted a petition for the same purpose. The petition was refused as, unlike St David's, there was no evidence of any charter or letters patent in the past conferring the status. Applications for city status in competitions in 2000 and 2002 were unsuccessful.
Unitary authorities of Wales
Unitary authority areas are styled as counties, except the City of Newport, the Cities and Counties of Cardiff and Swansea (all marked *), and the county boroughs (marked †). Welsh language forms are given in parentheses, except where there is no English equivalent.
|
|
|||||
Name changes
The current names of certain unitary authority areas are different from those specified in the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994. The following changes took place, all with effect from 2 April 1996 :
- Conwy from Aberconwy and Colwyn
- Isle of Anglesey from Anglesey
- Gwynedd from Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire
- Ceredigion from Cardiganshire
- Neath Port Talbot from Neath and Port Talbot
Communities
The lowest level of subdivision below unitary authority areas in Wales are Communities. Each area is subdivided into communities. They may have elected community councils (CCs) which perform a number of roles, such as providing local facilities, and representing their communities to larger local government bodies. Community councils are the equivalent of English parish councils. A community council may call itself a 'town council' if it wishes to do so. Two Welsh communities Bangor and St David's have city status and are therefore called 'City Councils'. Communities which are too small to have a council may have a community meeting instead, an example of direct democracy.
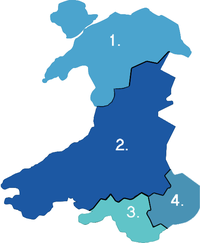
Police and fire services
Police forces
There are four police forces in Wales. These are:
 |
|
Fire and rescue services
There are three fire and rescue services in Wales. The present Welsh fire services date from 1996. Each covers a number of unitary authority areas. These are: