Khan Academy on a Stick
Polynomial and rational functions
Exploring quadratics and higher degree polynomials. Also in-depth look at rational functions.
-
 Factoring quadratic expressions
Factoring quadratic expressions
Factoring Quadratic Expressions
-
 Examples: Factoring simple quadratics
Examples: Factoring simple quadratics
A few examples of factoring quadratics
-
 Solving a quadratic equation by factoring
Solving a quadratic equation by factoring
U09_L2_T2_we1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring.avi
-
 Recognizing a perfect square quadratic
Recognizing a perfect square quadratic
U09_L2_T2_we2 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring 2.avi
-
 Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor
Example 1: Factoring trinomials with a common factor
Factoring trinomials with a common factor
-
 Factoring special products
Factoring special products
Factoring Special Products
-
 Example 1: Factoring difference of squares
Example 1: Factoring difference of squares
Factoring difference of squares
-
 Example 2: Factoring difference of squares
Example 2: Factoring difference of squares
Factoring difference of squares
-
 Factoring to produce difference of squares
Factoring to produce difference of squares
-
 Example 5: Factoring by grouping
Example 5: Factoring by grouping
Factoring Trinomials by Grouping 5
-
 Example 6: Factoring by grouping
Example 6: Factoring by grouping
Factoring Trinomials by Grouping 6
Factoring quadratics
Just saying the word "quadratic" will make you feel smart and powerful. Try it. Imagine how smart and powerful you would actually be if you know what a quadratic is. Even better, imagine being able to completely dominate these "quadratics" with new found powers of factorization. Well, dream no longer. This tutorial will be super fun. Just bring to it your equation solving skills, your ability to multiply binomials and a non-linear way of thinking!
-
 Solving quadratic equations by square roots
Solving quadratic equations by square roots
Solving Quadratic Equations by Square Roots
-
 Solving quadratic equations by completing the square
Solving quadratic equations by completing the square
Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
-
 How to use the quadratic formula
How to use the quadratic formula
Introduction to using the quadratic formula.
-
 Proof of quadratic formula
Proof of quadratic formula
Proof of Quadratic Formula
-
 Example: Complex roots for a quadratic
Example: Complex roots for a quadratic
Complex Roots from the Quadratic Formula
-
 Discriminant of quadratic equations
Discriminant of quadratic equations
Discriminant of Quadratic Equations
-
 Discriminant for types of solutions for a quadratic
Discriminant for types of solutions for a quadratic
Discriminant for Types of Solutions for a Quadratic
Completing the square and the quadratic formula
You're already familiar with factoring quadratics, but have begun to realize that it only is useful in certain cases. Well, this tutorial will introduce you to something far more powerful and general. Even better, it is the bridge to understanding and proving the famous quadratic formula. Welcome to the world of completing the square!
-
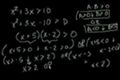 Quadratic inequalities
Quadratic inequalities
Solving quadratic inequalities using factoring
-
 Quadratic inequalities (visual explanation)
Quadratic inequalities (visual explanation)
How to solve a quadratic inequality. Visual intuition of what a quadratic inequality means.
Quadratic inequalities
You are familiar with factoring quadratic expressions and solving quadratic equations. Well, as you might guess, not everything in life has to be equal. In this short tutorial we will look at quadratic inequalities.
-
 Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial
Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial
Terms coefficients and exponents in a polynomial
-
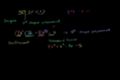 Addition and subtraction of polynomials
Addition and subtraction of polynomials
Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials
-
 Multiplying polynomials example
Multiplying polynomials example
Multiplying Polynomials
-
 Multiplying polynomials example 2
Multiplying polynomials example 2
Adding and multiplying polynomials
"Polynomials" sound like a fancy word, but you just have to break down the root words. "Poly" means "many". So we're just talking about "many nomials" and everyone knows what a "nomial" is. Okay, most of us don't. Well, a polynomials has "many" terms. From understanding what a "term" is to basic simplification, addition and subtraction of polynomials, this tutorial will get you very familiar with the world of many "nomials." :)
-
 Polynomial division
Polynomial division
Polynomial Division
-
 Polynomial divided by monomial
Polynomial divided by monomial
Polynomial divided by monomial
-
 Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial
Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial
Dividing multivariable polynomial with monomial
-
 Dividing polynomials 1
Dividing polynomials 1
Dividing polynomials 1
-
 Dividing polynomials with remainders
Dividing polynomials with remainders
Dividing polynomials with remainders
-
 Dividing polynomials with remainders example
Dividing polynomials with remainders example
-
 Polynomial remainder theorem to determine coefficient example
Polynomial remainder theorem to determine coefficient example
Dividing polynomials
You know what polynomials are. You know how to add, subtract, and multiply them. Unless you are completely incurious, you must be wondering how to divide them! In this tutorial we'll explore how we divide polynomials--both through algebraic long division and synthetic division. (We like classic algebraic long division more since you can actually understand what you're doing.)
-
 Synthetic division
Synthetic division
Basic algorithm for Synthetic Division
-
 Synthetic division example 2
Synthetic division example 2
Another example of applying the basic synthetic division algorithm
-
 Why synthetic division works
Why synthetic division works
Demonstrating why synthetic division gives you the same result as traditional algebraic long division
Synthetic division
In this tutorial, we'll learn a technique for dividing one polynomial by another--synthetic division. As always, we'll also explore why it works!
-
 Factoring sum of cubes
Factoring sum of cubes
Factoring Sum of Cubes
-
 Difference of cubes factoring
Difference of cubes factoring
u12 l2 t3 we2 Difference of Cubes Factoring
-
 Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression
Example: Factoring a fourth degree expression
Factoring Special Products 2
-
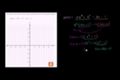 Factoring 5th degree polynomial to find real zeros
Factoring 5th degree polynomial to find real zeros
-
 Identifying graph based on roots
Identifying graph based on roots
Factoring and roots of higher degree polynomials
Factoring quadratics are now second nature to you. Even when traditional factoring is difficult, you know about completing the square and the quadratic formula. Now you're ready for something more interesting. Well, as you'll see in this tutorial, factoring higher degree polynomials is definitely the challenge you're looking for!
Polynomial graphs and end behavior
In this tutorial, we will study the behavior of polynomials and their graphs. In particular, we'll look at which forms of a polynomial are best for determining various aspects of its graph.
-
 Binomial theorem
Binomial theorem
-
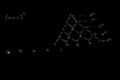 Pascal's triangle for binomial expansion
Pascal's triangle for binomial expansion
-
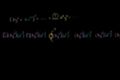 Determining coefficient in binomial expansion
Determining coefficient in binomial expansion
-
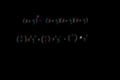 Intuitive connection between binomial expansion and combinatorics
Intuitive connection between binomial expansion and combinatorics
-
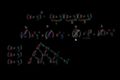 Connecting Pascal's triangle to binomial combinatorics
Connecting Pascal's triangle to binomial combinatorics
-
 Algorithm for mentally computing binomial expansion coefficients
Algorithm for mentally computing binomial expansion coefficients
-
 Binomial theorem combinatorics connection
Binomial theorem combinatorics connection
Intuition behind why binomial expansion involves combinatorics
Binomial theorem
You can keep taking the powers of a binomial by hand, but, as we'll see in this tutorial, there is a much more elegant way to do it using the binomial theorem and/or Pascal's Triangle.
-
 Simplifying rational expressions introduction
Simplifying rational expressions introduction
Simplifying Rational Expressions
-
 Simplifying rational expressions 1
Simplifying rational expressions 1
U11_L1_T1_we1 Simplifying Rational Expressions 1
-
 Simplifying rational expressions 2
Simplifying rational expressions 2
U11_L1_T1_we2 Simplifying Rational Expressions 2
-
 Simplifying rational expressions 3
Simplifying rational expressions 3
U11_L1_T1_we3 Simplifying Rational Expressions 3
Simplifying rational expressions
You get a rational expression when you divide one polynomial by another. If you have a good understanding of factoring quadratics, you'll be able to apply this skill here to help realize where a rational expression may not be defined and how we can go about simplifying it.
-
 Adding and subtracting rational expressions
Adding and subtracting rational expressions
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
-
 Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2
Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2
U11_L1_T3_we2 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 2
-
 Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3
Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3
U11_L1_T3_we3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 3
-
 Rational equations
Rational equations
Rational Equations
-
 Solving rational equations 1
Solving rational equations 1
Solving Rational Equations 1
-
 Solving rational equations 2
Solving rational equations 2
Solving Rational Equations 2
-
 Solving rational equations 3
Solving rational equations 3
Solving Rational Equations 3
-
 Subtracting rational expressions
Subtracting rational expressions
Subtracting Rational Expressions
-
 Applying rational equations 1
Applying rational equations 1
Applying Rational Equations 1
-
 Applying rational equations 2
Applying rational equations 2
Applying Rational Equations 2
-
 Applying rational equations 3
Applying rational equations 3
Applying Rational Equations 3
-
 Multiplying and simplifying rational expressions
Multiplying and simplifying rational expressions
Multiplying and Simplifying Rational Expressions
-
 Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1
Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1
-
 Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2
Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2
-
 Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3
Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3
-
 Extraneous solutions to rational equations
Extraneous solutions to rational equations
Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations
-
 Rational inequalities
Rational inequalities
Two ways to solve a rational inequality (or an inequality involving a fractional expression)
-
 Rational inequalities 2
Rational inequalities 2
Slightly harder rational inequality problem
Rational functions
Have you ever wondered what would happen if you divide one polynomial by another? What if you set that equal to something else? Would it be as unbelievably epic as you suspect it would be?
-
 Asymptotes of rational functions
Asymptotes of rational functions
Asymptotes of Rational Functions
-
 Another rational function graph example
Another rational function graph example
Another Rational Function Graph Example
-
 A third example of graphing a rational function
A third example of graphing a rational function
A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function
Asymptotes and graphing rational functions
-
 Partial fraction expansion 1
Partial fraction expansion 1
Introduction to partial fraction expansion
-
 Partial fraction expansion 2
Partial fraction expansion 2
A more complex problem
-
 Partial fraction expansion 3
Partial fraction expansion 3
Dealing with repeated factors
Partial fraction expansion
If you add several rational expressions with lower degree denominator, you are likely to get a sum with a higher degree denominator (which is the least-common multiple of the lower-degree ones). This tutorial lets us think about going the other way--start with a rational expression with a higher degree denominator and break it up as the sum of simpler rational expressions. This has many uses throughout mathematics. In particular, it is key when taking inverse Laplace transforms in differential equations (which you'll take, and rock, after calculus).
Advanced structure in expressions
This tutorial is all about *really* being able to interpret and see meaning in algebraic expressions--including those that involve rational expressions, exponentials, and polynomials. If you enjoy these ideas and problems, then you're really begun to develop your mathematical maturity.
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
This tutorial will better connect the world of complex numbers to roots of polynomials. It will show us that when we couldn't find roots, we just weren't looking hard enough. In particular, the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra tells us that every non-zero polynomial in one-variable of degree n has exactly n-roots (although they might not all be real!)
 Polynomial end behavior
Polynomial end behavior Polynomial end behavior example
Polynomial end behavior example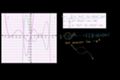 Another polynomial end behavior example
Another polynomial end behavior example Polynomial end behavior exercise example
Polynomial end behavior exercise example Structure in rational expression
Structure in rational expression Structure in exponential expression
Structure in exponential expression Fundamental theorem of algebra
Fundamental theorem of algebra Fundamental theorem of algebra for quadratic
Fundamental theorem of algebra for quadratic Possible number of real roots
Possible number of real roots