
Richard Francis Burton
Did you know...
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. Click here to find out about child sponsorship.
| Sir Richard Francis Burton | |
|---|---|
 Sir Richard Burton, portrait by Frederic Leighton, National Portrait Gallery |
|
| Born | March 19, 1821 Torquay, England |
| Died | October 20, 1890 (aged 69) Trieste, Italy |
| Resting place | St. Mary Magdalen's Church, London, England |
| Nationality | English |
| Known for | Exploration, Writing, Languages, Orientalist |
| Spouse(s) | Isabel Burton (1861-1890) |
Captain Sir Richard Francis Burton KCMG FRGS ( March 19, 1821 – October 20, 1890) was an English explorer, translator, writer, soldier, orientalist, ethnologist, linguist, poet, hypnotist, fencer and diplomat. He was known for his travels and explorations within Asia and Africa as well as his extraordinary knowledge of languages and cultures. According to one count, he spoke 29 European, Asian, and African languages.
Burton's best-known achievements include traveling in disguise to Mecca, making an unexpurgated translation of The Book of One Thousand Nights and A Night (the collection is more commonly called The Arabian Nights in English because of Andrew Lang's abridgment) and the Kama Sutra and journeying with John Hanning Speke as the first white men guided by the redoubtable Sidi Mubarak Bombay to discover (for himself and his contemporaries) the Great Lakes of Africa in search of the source of the Nile. He was a prolific author and wrote numerous books and scholarly articles about subjects including travel, fencing and ethnography.
He was a captain in the army of the East India Company serving in India (and later, briefly, in the Crimean War). Following this he was engaged by the Royal Geographical Society to explore the east coast of Africa and led an expedition guided by the locals which discovered Lake Tanganyika. In later life he served as British consul in Fernando Po, Damascus and, finally, Trieste. He was a Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society and was awarded a knighthood ( KCMG) in 1886.
Early life and education (1822–1841)
Burton was born in Torquay, Devon, at 21:30 on 19 March 1821; in his autobiography, he erroneously claimed to have been born in the family home at Barham House in Elstree in Hertfordshire. He was baptised on 2 September 1821 at Elstree Church in Borehamwood, Hertfordshire. His father, Lieutenant Colonel Joseph Netterville Burton, 36th Regiment, was an Irish-born British army officer of Anglo-Irish extraction, the son of the Rev. Edward Burton, a Church of Ireland clergyman from Westmorland, England, and an Irish mother; his mother, Martha Baker, was the heiress of a wealthy Hertfordshire squire, Richard Baker. Burton had two siblings, Maria Katherine Elizabeth Burton and Edward Joseph Netterville Burton, born in 1823 and 1824, respectively.
Burton's family travelled considerably during his childhood. In 1825, his family moved to Tours, France. Burton's early education was provided by various tutors employed by his parents. He first began a formal education in 1829 at a preparatory school on Richmond Green in Richmond, London run by Rev. Charles Delafosse. Over the next few years, his family travelled between England, France and Italy. Burton showed an early gift for languages and quickly learned French, Italian and Latin, as well as several dialects, such as Neapolitan. During his youth, he was rumoured to have carried on an affair with a young Romani (Gypsy) woman, even learning the rudiments of her language. Some adduce this as a possible reason why he was able later in life to learn Hindi and other Indic languages almost preternaturally quickly, as Romani is related to this language family. However, these same Indian languages are members of the Indo-European family of languages, along with English, French and German. The peregrinations of his youth may have encouraged Burton to regard himself as an outsider for much of his life. As he put it, "Do what thy manhood bids thee do, from none but self expect applause..."
Burton entered Trinity College, Oxford, in the autumn of 1840. Despite his intelligence and ability, he soon antagonized his teachers and peers. During his first term, he is said to have challenged another student to a duel after the latter mocked Burton's moustache. Burton continued to gratify his love of languages by studying Arabic; he also spent his time learning falconry and fencing. In 1842, he attended a steeplechase in deliberate violation of college rules and subsequently dared to tell the college authorities that students should be allowed to attend such events. Hoping to be merely " rusticated"—that is, suspended with the possibility of reinstatement, the punishment of some less provocative students who had visited the steeplechase— he was instead permanently expelled from Trinity College. In a final jab at the environment he had come to despise, Burton reportedly trampled the College's flower beds with his horse and carriage while departing Oxford.
Army career (1842–1853)
In his own words "fit for nothing but to be shot at for six pence a day", Burton enlisted in the army of the East India Company at the behest of his ex-college classmates who were already members. He hoped to fight in the first Afghan war but the conflict was over before he arrived in India. He was posted to the 18th Bombay Native Infantry based in Gujarat and under the command of General Sir Charles James Napier. While in India he became a proficient speaker of Hindustani, Gujarati Jatki/ Siraiki and Marathi as well as Persian and Arabic. His studies of Hindu culture had progressed to such an extent that "my Hindu teacher officially allowed me to wear the Janeu ( Brahmanical Thread)" although the truth of this has been questioned since it would usually have required long study, fasting and a partial shaving of the head. Burton had many peculiar habits that set him apart from other soldiers. While in the army, he kept a large menagerie of tame monkeys in the hopes of learning their language. He also earned the name "Ruffian Dick" for his "demonic ferocity as a fighter and because he had fought in single combat more enemies than perhaps any other man of his time."
He was appointed to the Sindh survey, where he learned to use the measuring equipment that would later be useful in his career as an explorer. At this time he began to travel in disguise. He adopted the alias of Mirza Abdullah and often fooled local people and fellow officers into failing to recognise him. It was at this point that he began to work as an agent for Napier and, although details of exactly what this work entailed are not known, it is known that he participated in an undercover investigation of a brothel said to be frequented by English soldiers where the prostitutes were young boys. His life-long interest in sexual practices led him to produce a detailed report which was later to cause trouble for Burton when subsequent readers of the report (which Burton had been assured would be kept secret) came to believe that Burton had, himself, participated in some of the practices described within his writing.
In March 1849 he returned to Europe on sick leave. In 1850 he wrote his first book Goa and the Blue Mountains, a guide to the Goa region. He travelled to Boulogne to visit the fencing school there and it was there where he first encountered his future wife Isabel Arundell, a young Catholic woman from a good family.
First explorations and journey to Mecca (1851–1853)
Motivated by his love of adventure, Burton got the approval of the Royal Geographical Society for an exploration of the area and he gained permission from the Board of Directors of the British East India Company to take leave from the army. His seven years in India gave Burton a familiarity with the customs and behaviour of Muslims and prepared him to attempt a Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca and, in this case, Medina). It was this journey, undertaken in 1853, which first made Burton famous. He had planned it whilst travelling disguised among the Muslims of Sindh, and had laboriously prepared for the ordeal by study and practice (including being circumcised to further lower the risk of being discovered).
Although Burton was not the first non-Muslim European to make the Hajj ( Ludovico di Barthema in 1503 is believed to hold that distinction), his pilgrimage is the most famous and the best documented of the time. He adopted various disguises including that of a Pashtun to account for any oddities in speech, but he still had to demonstrate an understanding of intricate Islamic ritual, and a familiarity with the minutiae of Eastern manners and etiquette. Burton's trek to Mecca was quite dangerous and his caravan was attacked by bandits (a common experience at the time). As he put it, although "...neither Koran or Sultan enjoin the death of Jew or Christian intruding within the columns that note the sanctuary limits, nothing could save a European detected by the populace, or one who after pilgrimage declared himself an unbeliever." The pilgrimage entitled him to the title of Hajji and to wear green head wrap. Burton's own account of his journey is given in A Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to Al-Medinah and Meccah (1855).
Some members of his entourage suspected there was more to Burton than met the eye. He came close to being discovered one night when he lifted his robe to urinate, rather than squatting as an Arab would. He thought he was unseen, but the youngest member of his group happened to see him. The lad accused him of being an imposter, but let Burton convince him to keep his doubts to himself.
When Burton returned to the British Army he sat for examination as an Arab linguist - and failed.
Early explorations (1854–1855)
Following his return to Cairo from Mecca, Burton sailed to India to rejoin his regiment. In March 1854, he transferred to the political department of the East India Company and went to Aden on the Arabian Peninsula in order to prepare for a new expedition, supported by the Royal Geographical Society, to explore the interior of the Somali Country and beyond, where Burton hoped to discover the large lakes he had heard about from Arab travelers. It was in Aden in September of this year that he first met Captain (then Lieutenant) John Hanning Speke who would accompany him on his most famous exploration. Burton undertook the first part of the trip alone. He made an expedition to Harar (in present day Ethiopia), which no European had entered (indeed there was a prophecy that the city would decline if a Christian was admitted inside). This leg of the expedition lasted three months, although much of the time was spent in the port of Zeila, where Burton, once again in disguise, awaited word that the road to Harar was safe. Burton not only travelled to Harar but also was introduced to the Emir and stayed in the city for ten days, officially a guest of the Emir but in reality his prisoner. The journey back was plagued by lack of supplies, and Burton wrote that he would have died of thirst had he not seen desert birds and realised they would be near water.
Following this adventure, he prepared to set out for the interior accompanied by Lieutenant Speke, Lieutenant G. E. Herne and Lieutenant William Stroyan and a number of Africans employed as bearers. However, before the expedition was able to leave camp, his party was attacked by a group of Somali tribesmen (the officers estimated the number of attackers at 200). In the ensuing fight, Stroyan was killed and Speke was captured and wounded in eleven places before he managed to escape. Burton was impaled with a javelin, the point entering one cheek and exiting the other. This wound left a notable scar that can be easily seen on portraits and photographs. He was forced to make his escape with the weapon still transfixing his head. However, the failure of this expedition was viewed harshly by the authorities, and a two-year investigation was set up to determine to what extent Burton was culpable for this disaster. While he was largely cleared of any blame, this did not help his career. He describes the harrowing attack in First Footsteps in East Africa (1856).
In 1855, Burton rejoined the army and travelled to the Crimea hoping to see active service in the Crimean War. He served on the staff of Beatson's Horse a corps of Bashi-bazouks, local fighters under the command of General Beatson, in the Dardanelles. The corps was disbanded following a "mutiny" after they refused to obey orders and Burton's name was mentioned (to his detriment) in the subsequent inquiry.
Exploring the lakes of central Africa (1856–1860)
In 1856 the Royal Geographical Society funded another expedition in which Burton set off from Zanzibar to explore an "inland sea" which was known to exist. His mission was to study local tribes and to find out what exports might be possible from the region. It was hoped that the expedition might lead to the discovery of the source of the River Nile, although this was not an explicit aim. Burton had been told that only a fool would say his expedition aimed to find the source of the Nile because anything short of that would be regarded as a failure.
Before leaving for Africa, Burton became secretly engaged to Isabel Arundell. Her family, particularly her mother, would not allow a marriage since Burton was not a Catholic and was not wealthy, although in time the relationship would become tolerated.
Speke again accompanied him and on the 27 June 1857 they set out from the east coast of Africa heading west in search of the lake or lakes. They were helped greatly by their experienced local guide, Sidi Mubarak (also known as "Bombay"), who was familiar with some of the customs and languages of the region. From the start the outward journey was beset with problems such as recruiting reliable bearers and the defalcation of equipment and supplies by deserting expedition members. Both men were beset by a variety of tropical diseases on the journey. Speke was rendered blind for some of the journey and deaf in one ear (due to an infection caused by attempts to remove a beetle). Burton was unable to walk for some of the journey and had to be carried by the bearers.
The expedition arrived at Lake Tanganyika in February 1858. Burton was awestruck by the sight of the magnificent lake, but Speke, who had been temporarily blinded by a disease, was unable to see the body of water. By this point much of their surveying equipment was lost, ruined, or stolen, and they were unable to complete surveys of the area as well as they wished. Burton was again taken ill on the return journey and Speke continued exploring without him, making a journey to the north and eventually locating the great Lake Victoria, or Victoria Nyanza. Lacking supplies and proper instruments Speke was unable to survey the area properly but was privately convinced that it was the long sought source of the Nile. Burton's description of the journey is given in Lake Regions of Equatorial Africa (1860). Speke gave his own account in The Journal of the Discovery of the Source of the Nile (1863).
Both Burton and Speke were in extremely poor health after the journey and returned home separately. As usual Burton kept very detailed notes, not just on the geography but also on the languages, customs and even sexual habits of the people he encountered. Although it was Burton's last great expedition his geographical and cultural notes were to prove invaluable for subsequent explorations by Speke and James Augustus Grant, Sir Samuel Baker, David Livingstone and Henry Morton Stanley. Speke and Grant's (1863) exploration began on the east coast near Zanzibar again and went around the west side of Lake Victoria to Lake Albert and finally returning in triumph via the Nile River. However, crucially, they had lost track of the river's course between Lake Victoria and Albert. This left Burton, and others, unsatisfied that the source of the Nile was conclusively proven.
Burton and Speke
Burton and Speke's exploration to Tanganyika and Victoria was, arguably, his most celebrated exploration but what followed was a prolonged public quarrel between the two men, which severely damaged Burton's reputation. From surviving letters it seems that Speke already mistrusted and disliked Burton before the start of their second expedition. There are several reasons why they became estranged. It seems obvious that the two men were very different in character, with Speke being more in tune with the prevailing morality of Victorian England and imperialistic attitude to other cultures. There was obviously a great element of professional rivalry. Some biographers have suggested that friends of Speke (particularly Laurence Oliphant) stirred up trouble between the two. It also seems that Speke resented Burton's position as expedition leader and claimed that this leadership was nominal only and that Burton was an invalid for most of the second expedition. There were problems with debts run up by the expedition that were left unpaid when they left Africa. Speke claimed that Burton had sole responsibility for these debts. Finally, there was the issue of the source of the Nile, perhaps the greatest prize of its day to explorers. It is now known that Lake Victoria is a source, but at the time the issue was controversial. Speke's expedition there was undertaken without Burton (who was incapacitated by several illnesses at the time) and his survey of the area was, by necessity, rudimentary, leaving the issue unresolved. Burton (and indeed many eminent explorers such as Livingstone) were very sceptical that the lake was the genuine source.
After the expedition, the two men travelled home to England separately with Speke arriving in London first. Despite an agreement between them that they would give their first public speech together, Speke gave a lecture at the Royal Geographical Society in which he made the claim that his discovery, Lake Victoria, was the source of the Nile. When Burton arrived in London he found Speke being lionised, and felt his own role was being considered as that of sickly companion. Furthermore, Speke was organising other expeditions to the region and clearly had no plans to include Burton.
In the subsequent months, Speke did much to attempt to harm Burton's reputation, even going so far as to claim that Burton had tried to poison him during the expedition. Meanwhile Burton spoke out against Speke's claim to have discovered the source of the Nile, saying that the evidence was inconclusive and the measurements made by Speke were inaccurate. It is notable that in Speke's expedition with Grant he made Grant sign a statement saying, amongst other things, "I renounce all my rights to publishing... my own account [of the expedition] until approved of by Captain Speke or the R. G. S. (Royal Geographical Society)".
Speke and Grant undertook a second expedition to prove that Lake Victoria was the true source of the Nile, but again, problems with surveying and measurement meant not everybody was satisfied the issue had been resolved. On 16 September 1864 Burton and Speke were due to debate the issue of the source of the Nile in front of the British Association for the Advancement of Science at that body's annual meeting in Bath. Burton was regarded as the superior public speaker and scholar and was likely to get the better of such a debate. However, the previous day Speke died from a self-inflicted gunshot wound while hunting on a relative's nearby estate. There were no direct witnesses to the shooting, and it has been widely speculated that he might have committed suicide; however, the coroner declared it to be a hunting accident. Burton was at the debate hall in Bath waiting to give his presentation when the news of Speke's death arrived and, considerably shaken, he elected not to give his planned talk.
Diplomatic service, scholarship, and death (1861–1890)
In January 1861, Richard and Isabel married in a quiet Catholic ceremony although he did not adopt the Catholic faith at this time. Shortly after this, the couple were forced to spend some time apart when he formally entered the Foreign Service as consul at Fernando Po, the modern island of Bioko in Equatorial Guinea. This was not a prestigious appointment; because the climate was considered extremely unhealthy for Europeans, Isabel could not accompany him. Burton spent much of this time exploring the coast of West Africa.
The couple were reunited in 1865 when Burton was transferred to Santos in Brazil. Once there, Burton traveled through Brazil's central highlands, canoeing down the Sao Francisco river from its source to the falls of Paulo Afonso.
In 1869 he was made consul in Damascus, an ideal post for someone with Burton's knowledge of the region and customs. However, Burton made many enemies during his time there. He managed to antagonize much of the Jewish population of the area because of a dispute concerning money lending. It had been the practice for the British consulate to take action against those who defaulted on loans but Burton saw no reason to continue this practice and this caused a great deal of hostility. He and Isabel greatly enjoyed their time there and befriended Lady Jane Digby, the well-known adventurer, and Abd al-Kader al-Jazairi, a prominent leader of the Algerian revolution then living in exile.
However, the area was in some turmoil at the time with considerable tensions between the Christian, Jewish and Muslim populations. Burton did his best to keep the peace and resolve the situation but this sometimes led him into trouble. On one occasion, he claims to have escaped an attack by hundreds of armed horsemen and camel riders sent by Mohammed Rashid Pasha, the Governor of Syria. He wrote "I have never been so flattered in my life than to think it would take three hundred men to kill me."
In addition to these incidents, there were a number of people who disliked Burton and wished him removed from such a sensitive position. Eventually, to resolve the situation, Burton was transferred to Trieste (then part of Austria-Hungary) during 1871. Burton was never particularly content with this post but it required little work and allowed him the freedom to write and travel.
In 1863 Burton co-founded the Anthropological Society of London with Dr. James Hunt. In Burton's own words, the main aim of the society (through the publication of the periodical Anthropologia) was "to supply travellers with an organ that would rescue their observations from the outer darkness of manuscript and print their curious information on social and sexual matters". On February 5, 1886 he was awarded a knighthood ( KCMG) by Queen Victoria.
He wrote a number of travel books in this period that were not particularly well received. His best-known contributions to literature were those considered risqué or even pornographic at the time and which were published under the auspices of the Kama Shastra society. These books include The Kama Sutra of Vatsyayana (1883) (popularly known as the Kama Sutra), The Book of the Thousand Nights and a Night (1885) (popularly known as The Arabian Nights), The Perfumed Garden of the Shaykh Nefzawi (1886) and The Supplemental Nights to the Thousand Nights and a Night (sixteen volumes 1886– 1898).
Published in this period, but composed on his return journey from Mecca, The Kasidah has been cited as evidence of Burton's status as a Sufi. The poem (and Burton's notes and commentary on it) contain layers of Sufic meaning, and seem to have been designed to project Sufi teaching in the West. "Do what thy manhood bids thee do/ from none but self expect applause;/ He noblest lives and noblest dies/ who makes and keeps his self-made laws" is The Kasidah's most oft-quoted passage.
Other works of note include a collection of Hindu tales, Vikram and the Vampire (1870); and his uncompleted history of swordsmanship, The Book of the Sword (1884). He also translated The Lusiads, the Portuguese national epic by Luís de Camões, in 1880 and wrote a sympathetic biography of the poet and adventurer the next year. The book The Jew, the Gipsy and el Islam was published posthumously in 1898 and was controversial since it was virulently anti-Semitic in tone and asserted the existence of Jewish human sacrifices. (Burton's investigations into this had provoked hostility from the Jewish population in Damascus, see Damascus affair. The manuscript of the book included an appendix discussing the topic in more detail, but by the decision of his widow it was not included in the book when published).
Burton died in Trieste early on the morning of 20 October 1890 of a heart attack. His wife Isabel persuaded a priest to perform the last rites, although Burton was not a Catholic and this action later caused a rift between Isabel and some of Burton's friends. It has been suggested that the death occurred very late on 19 October and that Burton was already dead by the time the last rites were administered.
Isabel never recovered from the loss. After his death she burned many of her husband's papers, including journals and a planned new translation of The Perfumed Garden to be called The Scented Garden, for which she had been offered six thousand guineas and which she regarded as his "magnum opus." She believed she was acting to protect her husband's reputation, and imagined she was instructed to burn the manuscript of The Scented Garden by his spirit, but her actions have been widely condemned.
Isabel wrote a biography in praise of her husband. The couple are buried in a remarkable tomb in the shape of a Bedouin tent at Mortlake in southwest London.
The Kama Shastra Society
Burton had long had an interest in sexuality and erotic literature. However, the Obscene Publications Act of 1857 had resulted in many jail sentences for publishers, with prosecutions being brought by the Society for the Suppression of Vice (Burton referred to the society and those who shared its views as Mrs Grundy). A way around this was the private circulation of books amongst the members of a society. For this reason Burton, together with Forster Fitzgerald Arbuthnot, created the Kama Shastra Society to print and circulate books that would be illegal to publish in public.
One of the most celebrated of all his books is his translation of the The Book of the Thousand Nights and a Night (more commonly known in English as The Arabian Nights because of Andrew Lang's abridged collection) in ten volumes, (1885) with six further volumes being added later. The volumes were printed by the Kama Shashtra Society in a subscribers-only edition of one thousand with a guarantee that there would never be a larger printing of the books in this form. The stories collected were often sexual in content and were considered pornography at the time of publication. In particular, the Terminal Essay of the Nights was one of the first English language texts to dare address the practice of pederasty which he postulated was prevalent in an area of the southern latitudes named by him the " Sotadic zone." Rumors about Burton’s own sexuality were already circulating and were further incited by this work.
Perhaps Burton's best-known book is his translation of The Kama Sutra. In fact, it is not really true that he was the translator since the original manuscript was in ancient Sanskrit which he could not read. However, he collaborated with Forster Fitzgerald Arbuthnot on the work and provided translations from other manuscripts of later translations. The Kama Shashtra Society first printed the book in 1883 and numerous editions of the Burton translation are in print to this day.
His English translation from a French edition of the Arabic erotic guide The Perfumed Garden was printed as The Perfumed Garden of the Cheikh Nefzaoui: A Manual of Arabian Erotology (1886). After Richard's death Isabel burnt many of his papers, including a manuscript of a subsequent translation, The Scented Garden, containing the final chapter of the work, on pederasty. It is interesting to note that Burton all along intended for this translation to be published after his death, to provide a competence for his widow, and also, as a final gesture of defiance against Victorian society.
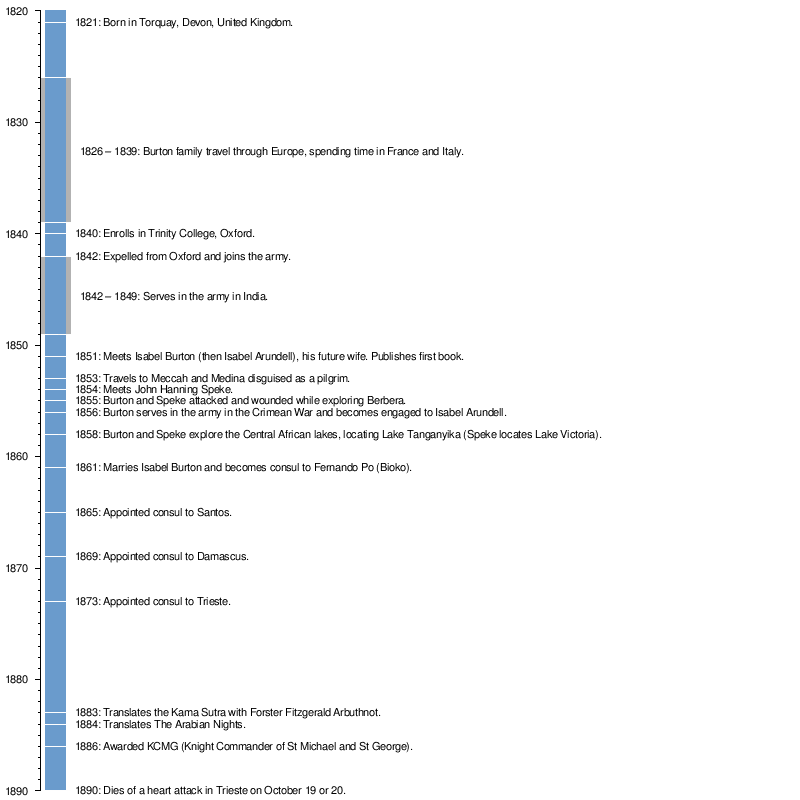
Chronology
Appearances in fiction and drama
Fiction
- There is a brief reference to Burton in Arthur Conan Doyle's novel The Lost World, which mentions Burton by name in the text but gives no information about him; when Doyle's novel was first published, Burton's exploits were comparatively recent.
- Philip José Farmer, a science fiction author, featured Burton as one of several protagonists in his Riverworld Saga (1966 – 1993).
- George MacDonald Fraser also mentions Burton repeatedly in his Flashman series (1969 – 2005) of historical novels (with the narrator, Flashman, usually referring to him as "that rogue Dick Burton").
- John Dunning includes Burton in his detective fiction The Bookman's Promise (Scribner 2004).
- Ilija Trojanow, Der Weltensammler, a German language novel features Richard Burton (Hanser 2006) English language translation "The Collector of Worlds" (Faber and Faber 2008).
- Robert Doherty's Area 51 novels (1997 – 2004) feature Burton as the discoverer of a secret alien race. The books include sections from Burton's writings.
- Wilkie Collins's detective novel The Moonstone (1859) features a character, Mr. Murthwaite, apparently based on Burton. He is "the celebrated Indian traveller, Mr. Murthwaite, who, at risk of his life, had penetrated in disguise where no European had ever set foot before" (chapter X).
- Karen Mercury's historical fiction novel The Four Quarters of the World (2006) has a hero based on Burton. After being speared through the jaw in Somaliland, he becomes the right-hand man to the Tewodros II of Abyssinia prior to the downfall of that empire.
- Richard Burton appears in the steampunk novel Larklight by Philip Reeve, in which he is portrayed as having "gone native" and taken a Martian wife.
- In The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen novel, Burton is implied to have been a member of a past League.
- Richard Burton is the leader of the Indians and settlers from Roanoke Island on the first island of the Underneath in James A. Owens' " The Search For the Red Dragon", the second book in the Chronicles of the Imaginarium Geographica.
Film
- Mountains of the Moon (1990) (starring Irish actor Patrick Bergin as Burton) related the story of the Burton-Speke exploration and the subsequent controversy over the source of the Nile. This was based on the 1984 novel Burton and Speke by William Harrison.
- Zero Patience (1993) re-imagines Burton in a contemporary setting as a closeted gay man obsessed with researching the Patient Zero hypothesis of AIDS transmission.
Television
- In The Sentinel (1996-1999) (starring Richard Burgi and Garett Maggart) a fictional monograph attributed to Richard Burton ("the explorer, not the actor") forms the background of the show's mythology.
- Search for the Nile, 1971 BBC mini-series featured Kenneth Haigh as Burton
- On the American television series Lost (episode 4x11, " Cabin Fever"), a photo of Burton appears in the high school locker of a teenaged John Locke.
- In The Victorian Sex Explorer, Rupert Everett documents Burton's travels. Part of the Channel Four (UK) 'Victorian Passions' season. First Broadcast on 9th June 2008.
Selected writings of Richard Francis Burton
- Goa and the Blue Mountains (1851)
- Scinde or the Unhappy Valley (1851)
- Sindh and the Races That Inhabit the Valley of the Indus (1851)
- Falconry in the Valley of the Indus (1852)
- A Complete System of Bayonet Exercise (1853)
- Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to Al Madinah and Meccah 3 Vols. (1855-6). See also PDF facsimile
- First Footsteps in East Africa (1856). See also PDF Facsimile .
- The Lake Regions of Central Equatorial Africa (1859)
- The Lake Regions of Central Africa (1860)
- The City of the Saints, Among the Mormons and Across the Rocky Mountains to California (1861)
- Wanderings in West Africa (1863)
- Abeokuta and the Cameroon Mountains (1863)
- A Mission to Gelele, King of Dahomé (1864)
- The Nile Basin (1864) With James McQueen.
- Wit and Wisdom From West Africa (1865)
- Stone Talk (1865)
- The Guide-book. A Pictorial Pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina (1865).
- Explorations of the Highlands of Brazil (1869)
- Letters From the Battlefields of Paraguay (1870)
- Vikram and the Vampire or Tales of Hindu Devilry (1870). See also PDF Facsimile.
- Unexplored Syria (1872)
- Zanzibar (1872)
- Ultima Thule (1872)
- The Lands of Cazembe. Lacerda's Journey to Cazembe in 1798 (1873). Edited and translated by Burton.
- The Captivity of Hans Stade of Hesse, in A.D. 1547-1555, Among the Wild Tribes of Eastern Brazil. Translated by Albert Tootal and annotated by Richard F. Burton.
- A New System of Sword Exercise for Infantry (1876)
- Two Trips to Gorilla Land and the Cataracts of the Congo (1876) See also PDF Facsimile.
- Etruscan Bologna (1876)
- Sind Revisited (1877)
- The Gold Mines of Midian (1878)
- The Land of Midian (revisited) (1879)
- Os Lusiadas (The Lusiads) (two volumes 1880)
- The Kasidah of Haji Abdu El-Yezdi (1880). See also PDF Facsimile.
- A Glance at the Passion-Play (1881).
- To the Gold Coast for Gold 2 Vols. (1883). See also PDF Facsimile.
- The Kama Sutra of Vatsyayana (1883) (with F. F. Arbuthnot).
- Camoens: His Life and His Lusiads (1883)
- Camoens. The Lyricks 2 Vols (1884)
- The Book of the Sword (1884)
- The Book of the Thousand Nights and a Night (ten volumes 1885)
- The Perfumed Garden of the Shaykh Nefzawi (1886)
- The Supplemental Nights to the Thousand Nights and a Night (six volumes 1886 – 1888)
- The Jew, the Gypsy and El Islam (1898)
- The Sentiment of the Sword: A Country-House Dialogue (1911)
Burton also wrote a great number of journal and magazine pieces, many of which have never been catalogued. Over 200 of these have been collected in PDF facsimile format at burtoniana.org.
Biographies and other books about Burton
A number of biographies of Burton have been written. The following is a list of biographies or books inspired by Burton, concentrating on those which are recent or influential.
- Brodie, Fawn M. (1967). The Devil Drives: A Life of Sir Richard Burton. New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
- Burton, Isabel (1893). The Life of Captain Sir Richard F. Burton KCMG, FRGS. Vols. 1 and 2. London: Chapman and Hall. http://burtoniana.org/biography/1893-Isabel-Life/index.html.
- Edwardes, Allen (1963). Death Rides a Camel. New York: The Julian Press.
- Farwell, Byron (1963). Burton: A Biography of Sir Richard Francis Burton. New York: Penguin Books.
- Harrison, William (1984). Burton and Speke. New York: St. Martin's Press.
- Lovell, Mary S. (1998). A Rage to Live: A Biography of Richard & Isabel Burton. New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
- McLynn, Frank (1993). Burton: Snow on the Desert. London: John Murray Publishing.
- McLynn, Frank (1990). Of No Country: An Anthology of Richard Burton. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons.
- Ondaatje, Christopher (1998). Journey to the Source of the Nile. Toronto: HarperCollins.
- Ondaatje, Christopher (1996). Sindh Revisited: A Journey in the Footsteps of Captain Sir Richard Francis Burton. Toronto: HarperCollins.
- Rice, Edward (1990). Captain Sir Richard Francis Burton: The Secret Agent Who Made the Pilgrimage to Makkah, Discovered the Kama Sutra, and Brought the Arabian Nights to the West. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons.
- Wright, Thomas (1906). The Life of Sir Richard Burton. Vols. 1 and 2. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons. http://etext.library.adelaide.edu.au/b/burton/richard/b97zw/.





