Organism
Background Information
SOS believes education gives a better chance in life to children in the developing world too. All children available for child sponsorship from SOS Children are looked after in a family home by the charity. Read more...


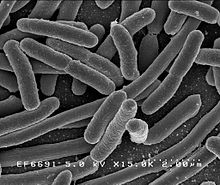
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system (such as animal, fungus, micro-organism, or plant). In at least some form, all types of organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homeostasis as a stable whole.
An organism may be either unicellular (a single cell) or, as in the case of humans, comprise many trillions of cells grouped into specialized tissues and organs. The term multicellular (many cells) describes any organism made up of more than one cell.
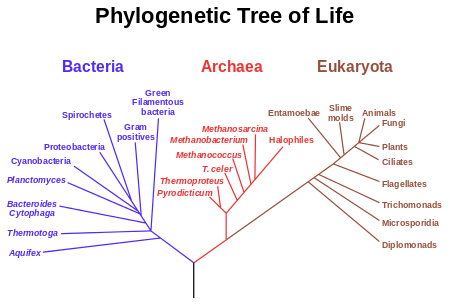
All organisms living on Earth are divided into the eukaryotes and prokaryotes based on the presence or absence of true nuclei in their cells. The prokaryotes represent two separate domains, the Bacteria and Archaea. Eukaryotic organisms, with a membrane-bounded cell nucleus, also contain organelles, namely mitochondria and (in plants) plastids, generally considered to be derived from endosymbiotic bacteria. Fungi, animals and plants are examples of species that are eukaryotes.
In 2002 Thomas Cavalier-Smith proposed a clade, Neomura, which groups together the Archaea and Eukarya. Neomura is thought to have evolved from Bacteria, more specifically from Actinobacteria. See Branching order of bacterial phyla.
Etymology
The term "organism" (Greek ὀργανισμός – organismos, from Ancient Greek ὄργανον – organon, "instrument, implement, tool, organ of sense or apprehension") first appeared in the English language in 1701 and took on its current definition by 1834 ( Oxford English Dictionary). It is directly related to the term "organization". There is a long tradition of defining organisms as self-organizing beings.
There has been a great deal of recent controversy about the best way to define the organism and indeed about whether or not such a definition is necessary. Several contributions are responses to the suggestion that the category of "organism" may well not be adequate in biology.
Semantics
The word organism may broadly be defined as an assembly of molecules functioning as a more or less stable whole that exhibits the properties of life. However, many sources propose definitions that exclude viruses and theoretically possible man-made non-organic life forms. Viruses are dependent on the biochemical machinery of a host cell for reproduction.
Chambers Online Reference provides a broad definition: "any living structure, such as a plant, animal, fungus or bacterium, capable of growth and reproduction".
In multicellular terms, "organism" usually describes the whole hierarchical assemblage of systems (for example circulatory, digestive, or reproductive) themselves collections of organs; these are, in turn, collections of tissues, which are themselves made of cells. In some plants and the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, individual cells are totipotent.
A superorganism is an organism consisting of many individuals working together as a single functional or social unit.
Non-cellular life
Viruses are not typically considered to be organisms because they are incapable of autonomous reproduction, growth or metabolism. This controversy is problematic because some cellular organisms are also incapable of independent survival (but not of independent metabolism and procreation) and live as obligatory intracellular parasites. Although viruses have a few enzymes and molecules characteristic of living organisms, they have no metabolism of their own and cannot synthesize and organize the organic compounds that form them. Naturally, this rules out autonomous reproduction and they can only be passively replicated by the machinery of the host cell. In this sense they are similar to inanimate matter. While viruses sustain no independent metabolism, and thus are usually not accounted organisms, they do have their own genes and they do evolve by similar mechanisms by which organisms evolve.
The most common argument in support of viruses as living organisms is their ability to undergo evolution and replicate through self-assembly. Some scientists argue that viruses neither evolve, nor self- reproduce. In fact, viruses are evolved by their host cells, meaning that there was co-evolution of viruses and host cells. If host cells did not exist, viral evolution would be impossible. This is not true for cells. If viruses did not exist, the direction of evolution could be different; however, the ability to evolve would not be affected. As for the reproduction, viruses totally rely on hosts' machinery to replicate themselves. The discovery of viral megagenoms with genes coding for energy metabolism and protein synthesis fueled the debate about whether viruses belong on the tree of life. The presence of these genes suggested that viruses could metabolize in the past. It was found later that the genes coding for energy and protein metabolism have cellular origin. Most likely, they were acquired through horizontal gene transfer from viral hosts.
Another good argument against placing viruses on the tree of life is their polyphyletic origin. Viruses do not share homologous characteristics neither with cellular organisms, nor with other viruses. Since it is impossible to trace viral evolution back to the last universal ancestor, it is also impossible to place them on the tree of life, which is based on the gene homology.
Organizational terminology
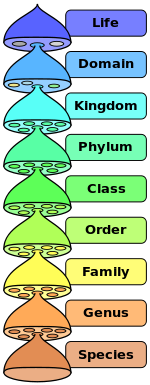
All organisms are classified by the science of alpha taxonomy into either taxa or clades.
Taxa are ranked groups of organisms, which run from the general ( domain) to the specific (species). A broad scheme of ranks in hierarchical order is:
To give an example, Homo sapiens is the Latin binomial equating to modern humans. All members of the species sapiens are, at least in theory, genetically able to interbreed. Several species may belong to a genus, but the members of different species within a genus are unable to interbreed to produce fertile offspring. Homo, however, only has one surviving species (sapiens), Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis, etc. having become extinct thousands of years ago. Several genera belong to the same family and so on up the hierarchy. Eventually, the relevant kingdom (Animalia, in the case of humans) is placed into one of the three domains depending upon certain genetic and structural characteristics.
All living organisms known to science are given classification by this system such that the species within a particular family are more closely related and genetically similar than the species within a particular phylum.
Since viruses are not living organisms, their classification is a challenging task. At first, viruses were classified according to their hosts: plant viruses, animal viruses, bacteriophages. Later, they were classified by the disease that they cause. For example, respiratory viruses, enterics. Now, viruses are classified based on the nucleic acid content, capsid symmetry and the presence or absence of the envelope.
Chemistry
Organisms are complex chemical systems, organized in ways that promote reproduction and some measure of sustainability or survival. The same laws that govern non-living chemistry govern the chemical processes of life. It is generally the phenomena of entire organisms that determine their fitness to an environment and therefore the survivability of their DNA-based genes.
Organisms clearly owe their origin, metabolism, and many other internal functions to chemical phenomena, especially the chemistry of large organic molecules. Organisms are complex systems of chemical compounds that, through interaction and environment, play a wide variety of roles.
Organisms are semi-closed chemical systems. Although they are individual units of life (as the definition requires), they are not closed to the environment around them. To operate they constantly take in and release energy. Autotrophs produce usable energy (in the form of organic compounds) using light from the sun or inorganic compounds while heterotrophs take in organic compounds from the environment.
The primary chemical element in these compounds is carbon. The physical properties of this element such as its great affinity for bonding with other small atoms, including other carbon atoms, and its small size making it capable of forming multiple bonds, make it ideal as the basis of organic life. It is able to form small three-atom compounds (such as carbon dioxide), as well as large chains of many thousands of atoms that can store data ( nucleic acids), hold cells together, and transmit information (protein).
Macromolecules
Compounds that make up organisms may be divided into macromolecules and other, smaller molecules. The four groups of macromolecule are nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. Nucleic acids (specifically deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA) store genetic data as a sequence of nucleotides. The particular sequence of the four different types of nucleotides ( adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine) dictate many characteristics that constitute the organism. The sequence is divided up into codons, each of which is a particular sequence of three nucleotides and corresponds to a particular amino acid. Thus a sequence of DNA codes for a particular protein that, due to the chemical properties of the amino acids it is made from, folds in a particular manner and so performs a particular function.
These protein functions have been recognized:
- Enzymes, which catalyze all of the reactions of metabolism
- Structural proteins, such as tubulin, or collagen
- Regulatory proteins, such as transcription factors or cyclins that regulate the cell cycle
- Signaling molecules or their receptors such as some hormones and their receptors
- Defensive proteins, which can include everything from antibodies of the immune system, to toxins (e.g., dendrotoxins of snakes), to proteins that include unusual amino acids like canavanine
Lipids make up the membrane of cells that constitutes a barrier, containing everything within the cell and preventing compounds from freely passing into, and out of, the cell.Due to the selective permeability of the phospholipid membraine only specific compounds can pass through it. In some multicellular organisms they serve as a storage of energy and mediate communication between cells. Carbohydrates are more easily broken down than lipids and yield more energy to compare to lipids and proteins.In fact, carbohydrates are the number one source of energy for all living organisms.
Structure
All organisms consist of monomeric units called cells; some contain a single cell (unicellular) and others contain many units (multicellular). Multicellular organisms are able to specialize cells to perform specific functions. A group of such cells is a tissue, and in animals these occur as four basic types, namely epithelium, nervous tissue, muscle tissue, and connective tissue. Several types of tissue work together in the form of an organ to produce a particular function (such as the pumping of the blood by the heart, or as a barrier to the environment as the skin). This pattern continues to a higher level with several organs functioning as an organ system to allow for reproduction, digestion, etc. Many multicell organisms consist of several organ systems, which coordinate to allow for life.
Cell
The cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Schleiden and Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells; all cells come from preexisting cells; all vital functions of an organism occur within cells, and cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells.
There are two types of cells, eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are usually singletons, while eukaryotic cells are usually found in multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells lack a nuclear membrane so DNA is unbound within the cell, eukaryotic cells have nuclear membranes.
All cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have a membrane, which envelops the cell, separates its interior from its environment, regulates what moves in and out, and maintains the electric potential of the cell. Inside the membrane, a salty cytoplasm takes up most of the cell volume. All cells possess DNA, the hereditary material of genes, and RNA, containing the information necessary to build various proteins such as enzymes, the cell's primary machinery. There are also other kinds of biomolecules in cells.
All cells share several similar characteristics of:
- Reproduction by cell division ( binary fission, mitosis or meiosis).
- Use of enzymes and other proteins coded by DNA genes and made via messenger RNA intermediates and ribosomes.
- Metabolism, including taking in raw materials, building cell components, converting energy, molecules and releasing by-products. The functioning of a cell depends upon its ability to extract and use chemical energy stored in organic molecules. This energy is derived from metabolic pathways.
- Response to external and internal stimuli such as changes in temperature, pH or nutrient levels.
- Cell contents are contained within a cell surface membrane that contains proteins and a lipid bilayer.
Life span
One of the basic parameters of an organism is its life span. Some organisms live as short as one day, while some plants and fungi can live thousands of years.
Evolution
In biology, the theory of universal common descent proposes that all organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor or ancestral gene pool. Evidence for common descent may be found in traits shared between all living organisms. In Darwin's day, the evidence of shared traits was based solely on visible observation of morphologic similarities, such as the fact that all birds have wings, even those that do not fly.
Today, there is debate over whether or not all organisms descended from a common ancestor, or a " last universal ancestor" (LUA), also called the "last universal common ancestor" (LUCA), the hypothetical unicellular organism or single cell that gave rise to all life on Earth 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago. The universality of genetic coding suggests common ancestry. For example, every living cell makes use of nucleic acids as its genetic material, and uses the same twenty amino acids as the building blocks for proteins, although exceptions to the basic twenty amino acids have been found. However, throughout history groupings based on appearance or function of species have sometimes been polyphyletic due to convergent evolution.
It was once thought that the genetic code was invariably universal (see: Universal genetic code), but many variations have been discovered including various alternative mitochondrial codes. Back in the early 1970s, evolutionary biologists thought that a given piece of DNA specified the same protein subunit in every living thing, and that the genetic code was thus universal. This was interpreted as evidence that every organism had inherited its genetic code from a single common ancestor, aka, an LUCA. In 1979, however, exceptions to the code were found in mitochondria, the tiny energy factories inside cells. Researchers studying human mitochondrial genes discovered that they used an alternative code, and many slight variants have been discovered since, including various alternative mitochondrial codes, as well as small variants such as Mycoplasma translating the codon UGA as tryptophan. Biologists subsequently found exceptions in bacteria and in the nuclei of algae and single-cell animals. For example, certain proteins may use alternative initiation (start) codons not normally used by that species. In certain proteins, non-standard amino acids are substituted for standard stop codons, depending upon associated signal sequences in the messenger RNA: UGA can code for selenocysteine and UAG can code for pyrrolysine. Selenocysteine is now viewed as the 21st amino acid, and pyrrolysine is viewed as the 22nd. A detailed description of variations in the genetic code can be found at the NCBI web site.
Information about the early development of life includes input from many different fields, including geology and planetary science. These sciences provide information about the history of the Earth and the changes produced by life. However, a great deal of information about the early Earth has been destroyed by geological processes over the course of time.
History of life
The chemical evolution from self-catalytic chemical reactions to life (see Origin of life) is not a part of biological evolution, but it is unclear at which point such increasingly complex sets of reactions became what we would consider, today, to be living organisms.

Little is known about the earliest developments in life. However, all existing organisms share certain traits, including cellular structure and genetic code. Most scientists interpret this to mean all existing organisms share a common ancestor, which had already developed the most fundamental cellular processes, but there is no scientific consensus on the relationship of the three domains of life (Archaea, Bacteria, Eukaryota) or the origin of life. Attempts to shed light on the earliest history of life generally focus on the behaviour of macromolecules, particularly RNA, and the behaviour of complex systems.
The emergence of oxygenic photosynthesis (around 3 billion years ago) and the subsequent emergence of an oxygen-rich, non-reducing atmosphere can be traced through the formation of banded iron deposits, and later red beds of iron oxides. This was a necessary prerequisite for the development of aerobic cellular respiration, believed to have emerged around 2 billion years ago.
In the last billion years, simple multicellular plants and animals began to appear in the oceans. Soon after the emergence of the first animals, the Cambrian explosion (a period of unrivaled and remarkable, but brief, organismal diversity documented in the fossils found at the Burgess Shale) saw the creation of all the major body plans, or phyla, of modern animals. This event is now believed to have been triggered by the development of the Hox genes. About 500 million years ago, plants and fungi colonized the land, and were soon followed by arthropods and other animals, leading to the development of today's land ecosystems.
The evolutionary process may be exceedingly slow. Fossil evidence indicates that the diversity and complexity of modern life has developed over much of the history of the earth. Geological evidence indicates that the Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Studies on guppies by David Reznick at the University of California, Riverside, however, have shown that the rate of evolution through natural selection can proceed 10 thousand to 10 million times faster than what is indicated in the fossil record. Such comparative studies however are invariably biased by disparities in the time scales over which evolutionary change is measured in the laboratory, field experiments, and the fossil record.
Horizontal gene transfer
The ancestry of living organisms has traditionally been reconstructed from morphology, but is increasingly supplemented with phylogenetics—the reconstruction of phylogenies by the comparison of genetic (DNA) sequence.
Sequence comparisons suggest recent horizontal transfer of many genes among diverse species including across the boundaries of phylogenetic "domains". Thus determining the phylogenetic history of a species can not be done conclusively by determining evolutionary trees for single genes.
Biologist Gogarten suggests "the original metaphor of a tree no longer fits the data from recent genome research", therefore "biologists (should) use the metaphor of a mosaic to describe the different histories combined in individual genomes and use (the) metaphor of a net to visualize the rich exchange and cooperative effects of HGT among microbes."
Future of life (cloning and synthetic organisms)
In modern terms, the category of organism cloning refers to the procedure of creating a new multicellular organism, genetically identical to another. However, cloning also has the potential of creating entirely new species of organisms. Organism cloning is the subject of much ethical debate. (see Bioethics, Ethics of cloning, and Designer baby articles)
In 2008 the J. Craig Venter Institute assembled a synthetic bacterial genome, Mycoplasma genitalium, by using recombination in yeast of 25 overlapping DNA fragments in a single step. "The use of yeast recombination greatly simplifies the assembly of large DNA molecules from both synthetic and natural fragments." Other companies, such as Synthetic Genomics, have already been formed to take advantage of the many commercial uses of custom designed genomes.