|
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
Summary
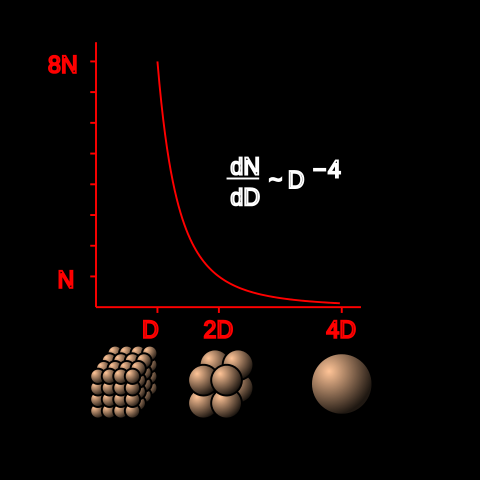
Illustration of the power law for the distribution of sizes in the Kuiper Belt. Plotted by a program written by Eurocommuter.
The curve represents the number of objects as a function of their diameter.
- Vertical axis: number of objects
- Horizontal axis: diameter
As illustration, for an object with diameter 4D, there should be 8 objects with diameter 2D and 64 objects with diameter D.
Neglecting smaller order terms, N ~ D - 3
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses:
 |
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License. http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue
|
You may select the license of your choice.
|
File usage
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
SOS Children's Villages aims to make Wikipedia suitable for young learners. By supporting vulnerable children right through to adulthood, SOS Children makes a lasting difference to the lives of thousands of people. Education is a key part of our work, and our schools provide high-quality teaching to the children in our care. Help another child by taking out a sponsorship.