Khan Academy on a Stick
Electricity and magnetism
-
 Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to charge and Coulomb's law
Electrostatics (part 1): Introduction to charge and Coulomb's law
Introduction to Charge and Coulomb's Law (video from May 2008 that I forgot to upload)
-
 Electrostatics (part 2)
Electrostatics (part 2)
Electric Fields
-
 Proof (advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1)
Proof (advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 1)
Electric field generated by a uniformly charged, infinite plate
-
 Proof (advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2)
Proof (advanced): Field from infinite plate (part 2)
We see that the infinite, uniformly charged plate generates a constant electric field (independent of the height above the plate)
-
 Electric potential energy
Electric potential energy
Introduction to electric potential
-
 Electric potential energy (part 2-- involves calculus)
Electric potential energy (part 2-- involves calculus)
Electric potential energy difference in a varying field
-
 Voltage
Voltage
Difference between electrical potential (voltage) and electrical potential energy
-
 Capacitance
Capacitance
Introduction to the capacitance of a two place capacitor.
-
 Circuits (part 1)
Circuits (part 1)
Introduction to electricity, circuits, current and resistance
-
 Circuits (part 2)
Circuits (part 2)
Resistors in series
-
 Circuits (part 3)
Circuits (part 3)
Resistors in parallel
-
 Circuits (part 4)
Circuits (part 4)
A hairy resistance problem
-
 Cross product 1
Cross product 1
Introduction to the cross product
-
 Cross product 2
Cross product 2
A little more intuition on the cross product.
-
 Cross product and torque
Cross product and torque
The cross product and the direction of torque.
-
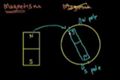 Introduction to magnetism
Introduction to magnetism
An introduction to magnetism
-
 Magnetism 2
Magnetism 2
Magnetic fields and their effects on moving electrical charges
-
 Magnetism 3
Magnetism 3
Whats happens when a speeding proton goes through a magnetic field
-
 Magnetism 4
Magnetism 4
Part 2 of the proton through a magnetic field problem
-
 Magnetism 5
Magnetism 5
Magnetic force on a wire carrying current.
-
 Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current
Magnetism 6: Magnetic field due to current
See how a wire carrying a current creates a magnetic field.
-
 Magnetism 7
Magnetism 7
The magnetic force that two current-carrying wires exert on each other.
-
 Magnetism 8
Magnetism 8
More on the forces exerted by 2 current carrying wires on each other.
-
 Magnetism 9: Electric motors
Magnetism 9: Electric motors
Using a magnetic field to exert torque on a rotating circuit.
-
 Magnetism 10: Electric motors
Magnetism 10: Electric motors
Why the circuit will keep flipping over.
-
 Magnetism 11: Electric motors
Magnetism 11: Electric motors
Using a commutator to solve the flipping problem and create an electric motor.
-
 Magnetism 12: Induced current in a wire
Magnetism 12: Induced current in a wire
Induced current and EMF in a moving wire from a magnetic field.
-
 The dot product
The dot product
Introduction to the vector dot product.
-
 Dot vs. cross product
Dot vs. cross product
Understanding the differences between the dot and cross products
-
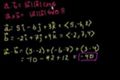 Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation
Calculating dot and cross products with unit vector notation
Calculating the dot and cross products when vectors are presented in their x, y, and z (or i,j, and k) components.